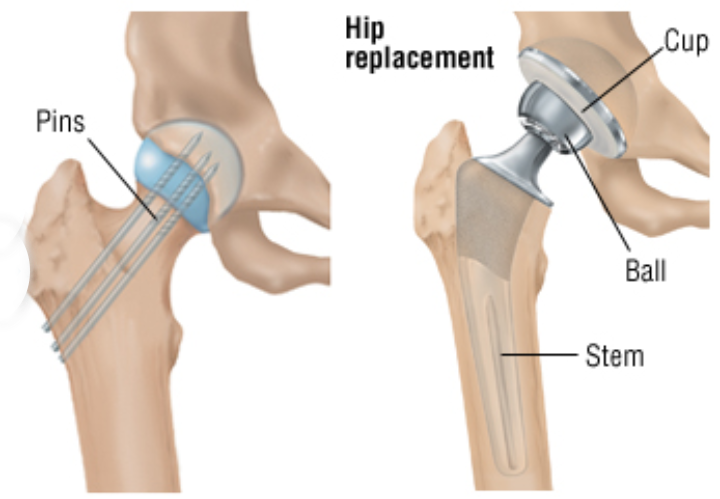
Hip Bone Broke Off
Scapula Bone Anatomy and Muscles. Anatomy of Scapula Bone. The scapula, also known as the shoulder blade is a triangular, flat bone of shoulder girdle that articulates with the head of humerus humerus at the glenohumeral joint which is popularly called as shoulder joint, and with the lateral end of clavicle at the acromioclavicular joint. In doing so, the scapula connects the upper limb to the trunk. Following diagram would explain the relation of scapula to thorax. Image Credit Wikipedia, Public domain. Scapula has got two surfaces, three borders, three angles and three processes. Scapula serves as a site for attachment for many important muscle around shoulder. Image Credit Wikipedia. Pediatric Orthopaedic Society of North America POSNA 9400 West Higgins Road, Suite 500 Rosemont, IL 600184976 p 847 6981692 f 847 8230536. Information from a patient of FAI Femoroacetabular impingement I had right hip FAI removal CAM type impingement labral tear repair surgery on June 14, 2010. The Surfaces of Scapula. Scapula has got two surfaces costal surface that abuts the thorax and dorsal surface which can be felt when we palpate the bone behind. The Costal surface. I/61cZKaLLQUL._SS500_.jpg' alt='Hip Bone Broke Off In Knee' title='Hip Bone Broke Off In Knee' />Costal surface of scapula is concave and is directed medially and forwards. A concave depression over most of its surface is called the subscapular fossa. The subscapularis muscle, one of the rotator cuff muscles, originates from this side. Coracoid process is a hook like projection originating from the superolateral surface of the costal scapula which lies just underneath the clavicle. Coatal surface is is marked by three longitudinal ridges. Another thick ridge adjoins the lateral border. This part of the bone is almost rod like. It acts as a lever for the action of the serratus anterior in overhead abduction of the arm. This surface gives attachment to the spine of the scapula which divides the surface into a smaller supraspinous fossa and a larger infraspinous fossa. The two fossae are connected by the spinoglenoid notch, situated lateral to the root of the spine. Acromion is the projection of the spine that arches over the glenohumeral joint and articulates with the clavicle. Image Credit Highlands. Borders, Angles and Processes of Scapula. Scapula has three borders. See diagram for locationThe Borders. Superior border of scapula is thin and short. It has suprascapular notch near the root of coracoid process. Lateral border of scapula is thick and presents the infraglenoid tubercle at the upper end. Medial border is thin extends from the superior angle to the inferior angle. The Angles. The superior angle is covered by the trapezius. The inferior angle is covered by the latissimus dorsi and moves forward round the chest when the arm is abducted. The lateral angle is broad and bears the glenoid cavity which is directed forwards, laterally and slightly upwards. Glenoid cavity articulates with head of humerus to form shoulder joint. The processes. The spinous process or spine of scapula is triangular plate of bone with three borders and two surfaces. It divides the dorsal surface of the scapula into the supraspinous and infraspinous fossae. Its posterior border is called the crest of the spine. The crest has upper and lower lips. The acromion process has two borders, medial and lateral, two surfaces, superior and inferior, and a facet for the clavicle. Coracoids process is directed forwards and slightly laterally and plays important role in shoulder stabilization by providing attachments to ligaments and muscles. How to Determine Side of ScapulaThe lateral angle is large and bears the glenoid cavity. The dorsal surface is convex and is divided by the triangular spine into the supraspinous and infraspinous fossae. The costal surface is concave to fit on the convex chest wall. The lateral thickest border runs from the glenoid cavity above to the inferior angle below. Muscles and Ligaments of Scapula. Various muscles and ligaments attach on scapula that are used to stabilize and move the bone. Setup.Exe Lost Planet 3. Movement of scapula helps in movements of shoulder joint. Muscles of Scapula. Image Credit Health Favo. Subscapularis Muscle. It arises from the medial two thirds of the subscapular fossa. Serratus Anterior Serratus anterior muscle is inserted along the medial border of the costal surface one digitations to the superior angle, two digitations to the medial border, and five digitations to the inferior angle. Supraspinatus Muscle. It arises from the medial two thirds of the supraspinous fossa including the upper surface of the spine. Infraspinatus Musclearises from the medial two thirds of the infraspinous fossa including the lower surface of the spine. Deltoid Muscle. Deltoid muscle arises from the lower border of the crest of the spine and from the lateral border of the acromion. Trapezius. Trapezius muscle is inserted into the upper border of the crest of the spine and into the medial border of the acromion. Biceps. The long head of the biceps arises from the supraglenoid tubercle. The short head from the lateral part of the tip of the coracoid process. Coracobrachialis. The coracobrachialis arises from the medial part of the tip of the coracoid process. Training Management System Pdf. Pectoralis Minor. Pectoralis minor is inserted into the medial border and superior surface of the coracoid process. Triceps. The long head of the triceps arises from the infraglenoid tubercle. Teres Minor. Teres minor arises from the upper two thirds of the rough strip on the dorsal surface along the lateral border. Teres Major. It arises from the lower one third of the rough strip on the lateral aspect of the lateral border. Levator Scapulaeis inserted along the dorsal aspect of the media border, from the superior angle up to the root of the spine. Rhomboideus Minor. It is inserted into the medial border dorsal aspect opposite the root of the spine of scapula. Rhomboideus Major. Het Meisje In De Trein Epub. Rhomboideus majorr is inserted into the medial border dorsal aspect between the root of the spine and the inferior angle. Omohyoid. The inferior belly of the omohyoid arises from the upper border near the suprascapular notch. Ligaments of Scapula. The margin of the glenoid cavity gives attachment to the capsule of the shoulder joint and to the glenoid labrum. The margin of the facet on the medial aspect of the acromion gives attachment to the capsule of the acromioclavicular joint. The coracoacromial ligament is attached. To the lateral border of the coracoid process, and. To the medial side of the tip of the acromion process. The coracohumeral ligament is attached to the root of the coracoid process. The coracoclavicular ligament is attached to the coracoid process the trapezoid part on the superior aspect, and the conoid part near the root. The suprascapular ligament bridges across the suprascapular notch and converts it into a foramen which transmits the suprascapular nerve. The suprascapular vessels lie above the ligament. The spinoglenoid ligament bridges the spino glenoid notch. The suprascapular vessels and nerve pass deep to it. Clinical Significance of Scapula. Paralysis of the serratus anterior cause winging of the scapula. The medial border of the bone becomes unduly prominent, and the arm cannot be abducted. In a developmental anomaly called scaphoid scapula, the medial border is concave. Scapula bone is frequently injured in trauma. Get more stuff on Musculoskeltal Health. Subscribe to our Newsletter and get latest publications on Musculoskeletal Health your email inbox. Thank you for subscribing. We respect your privacy and take protecting it seriously.